Humans and chimpanzees split from their last common ancestor several hundred thousand years earlier than believed, according to new research regarding pre-humans by an international team that includes University of Toronto’s David Begun.
Not only that, their findings indicate that the split occurred not in Africa — as customarily assumed — but in Europe.
“Our discovery outlines a new scenario for the beginning of human history,” said Begun, a paleoanthropologist in the Department of Anthropology in the Faculty of Arts & Science. Begun is co-author of one of two studies reported this week in PLOS ONE. “The findings allow us to move the human-chimpanzee split into the Mediterranean area.”
Dental roots give new evidence
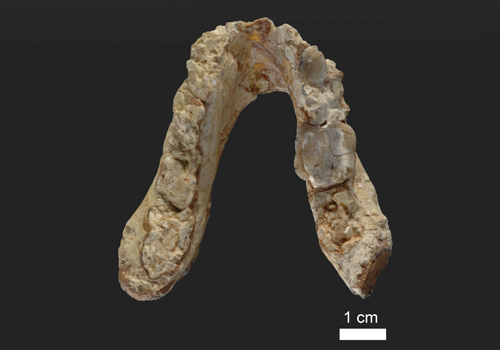
The researchers analyzed two known fossil specimens of Graecopithecus freybergi using state-of-the-art methods — a lower jaw from Greece and an upper premolar from Bulgaria — and came to the conclusion that they belong to pre-humans. Using computer tomography, they visualized the internal structures of the fossils and demonstrated that the roots of premolars are widely fused.
“While great apes typically have two or three separate and diverging roots, the roots of Graecopithecus converge and are partially fused — a feature that is characteristic of modern humans, early humans and several pre-humans including Ardipithecus and Australopithecus”, said Madelaine Böhme from the Senckenberg Centre for Human Evolution and Palaeoenvironment at the University of Tübingen, who co-led the investigations with Nikolai Spassov from the Bulgarian Academy of Sciences.
The lower jaw, nicknamed ‘El Graeco’ by the scientists, has additional dental root features, suggesting that the species Graecopithecus freybergi might belong to the pre-human lineage. The researchers were surprised by their results, as pre-humans were previously known only from sub-Saharan Africa.
Furthermore, Graecopithecus is several hundred thousand years older than the oldest potential pre-human from Africa, the six to seven-million-year-old Sahelanthropus from Chad.
The research team, which also included scientists from Greece, France and Australia, dated the sedimentary sequence of the Graecopithecus fossil sites in Greece and Bulgaria with physical methods and got a nearly synchronous age for both fossils — 7.24 and 7.175 million years before present.
Weakening the out-of-Africa theory

“It is at the beginning of the Messinian, an age that ends with the complete desiccation of the Mediterranean Sea,” Böhme said.
“These research findings call into question one of the most dogmatic assertions in paleoanthropology since Charles Darwin, which is that the human lineage originated in Africa,” said Begun.
Present-day chimpanzees are humans’ nearest living relatives. Where the last chimp-human common ancestor lived, however, is a central and highly debated issue in palaeoanthropology. Researchers have assumed up to now that the lineages diverged five to seven million years ago and that the first pre-humans developed in Eastern Africa. According to the 1994 theory of French palaeoanthropologist Yves Coppens, climate change in the region could have played a crucial role.
“It is not a matter of continental bragging rights,” Begun said. “It is critical to know where the human lineage arose so that we can reconstruct the circumstances leading to our divergence from the common ancestor we share with chimpanzees. Not having this information is like having a crime without the crime scene.”
Environmental changes the driving force for divergence
As with many animals, the evolution of pre-humans was driven by dramatic environmental changes. The team led by Böhme demonstrated that the North African Sahara desert originated more than seven million years ago. They concluded this based on geological analyses of the sediments in which the two fossils of Graecopithecus were found. Although geographically distant from the Sahara, the red-coloured silts are very fine-grained and could be classified as desert dust. An analysis of uranium, thorium, and lead isotopes in individual dust particles yields an age between 0.6 and 3 billion years and infers an origin in Northern Africa.
Moreover, the dusty sediment has a high content of different salts. The data document for the first time a spreading Sahara 7.2 million years ago, whose desert storms transported red, salty dusts to the north coast of what was then the Mediterranean Sea.
This process is also observable today. However, the researchers’ modelling shows that the dust in the past was more than 10 times the amount of recent dust loadings in Southern Europe —comparable to the present-day Sahel zone in Africa that marks the transition between the Sahara and the Sudan region.
Fire, grass, and water stress
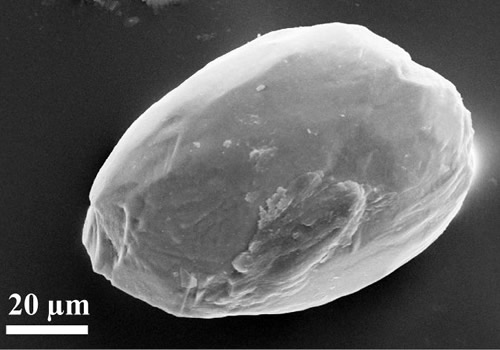
The researchers further showed that while the Sahara was developing in North Africa, a savannah biome was formed in Europe. Using a combination of new methodologies, they studied microscopic fragments of charcoal and plant silicate particles, called phytoliths.
Many of these phytoliths derive from grasses and particularly from those that use the metabolic pathway of C4-photosynthesis, which is common in today’s tropical grasslands and savannahs. The global spread of C4-grasses began eight million years ago on the Indian subcontinent — their presence in Europe was previously unknown.
The record they provide gives evidence of severe droughts, and the charcoal analysis indicates recurring vegetation fires.
“In summary, we reconstruct a savannah, which fits with the giraffes, gazelles, antelopes, and rhinoceroses that were found together with Graecopithecus,” said Spassov.
“The incipient formation of a desert in North Africa more than seven million years ago and the spread of savannahs in Southern Europe may have played a central role in the splitting of the human and chimpanzee lineages,” said Böhme. She calls this hypothesis the North Side Story, recalling the thesis of Yves Coppens, known as East Side Story.
“Researchers need to be more open minded in the quest to uncover the origins of the human lineage. This fossil shows that Europe is just as likely to hold the key to the answer to this eternal question as Africa,” said Begun.
The findings are described in two studies published in PLOS ONE titled “Potential hominin affinities of Graecopithecus from the late Miocene of Europe” and “Messinian age and savannah environment of the possible hominin Graecopithecus from Europe.”
With files from University of Tübingen.